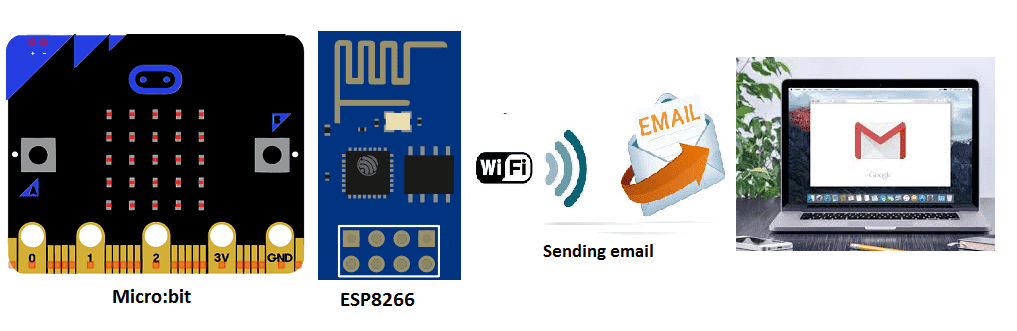
Sending an email using Micro:bit

ThingSpeak overview
ThingSpeak is an open-source Internet of Things (IoT) application and API that allows users to collect and store sensor data in the cloud and perform analytics on that data. It allows users to create “channels” to collect data from multiple sensors, and also has built-in support for visualizing and analyzing the data. ThingSpeak can be used for a variety of applications, such as monitoring environmental conditions, tracking the location of assets, and controlling devices remotely. It is available for free and also has paid subscription plans for additional features and support.
IFTTT overview
IFTTT (If This Then That) is a web-based service that allows users to create connections between different apps and devices, known as “applets”. These connections, or “recipes”, are triggered by a specific event or action, such as a change in weather or a new post on social media, and then perform a specific action, such as sending a notification or turning on a device.
For example, you could create an applet that sends you a text message whenever there is a severe weather warning in your area, or another applet that saves a copy of all your Instagram photos to a cloud storage service like Dropbox.
IFTTT supports a wide range of apps and services, including popular ones like Facebook, Twitter, Gmail, and Nest, as well as IoT devices like Philips Hue and Belkin WeMo. You can also create your own custom applets using the IFTTT Webhooks service.
Purpose of this tutorial:
The Micro:bit is a small, programmable computer that can be used to control various electronic devices and sensors. Sending an email using a Micro:bit requires a few additional components and a bit of programming.
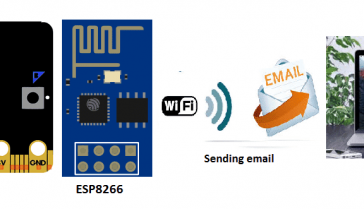
One way to send an email using a Micro:bit is to connect it to a Wi-Fi module, such as the ESP8266. This module allows the Micro:bit to connect to a Wi-Fi network and send data over the internet.
Once is to use a service like Thingspeak and IFTTT which allows you to create “recipes” that trigger actions based on inputs from connected devices such as the Micro:bit. These services typically provide a simple API that can be used to send data from the Micro:bit to the internet, allowing you to trigger an email to be sent.
In any case, sending an email using a Micro:bit requires some knowledge of programming and networking, as well as an understanding of how email works. It is not an easy task, but with proper guide and experience is possible.
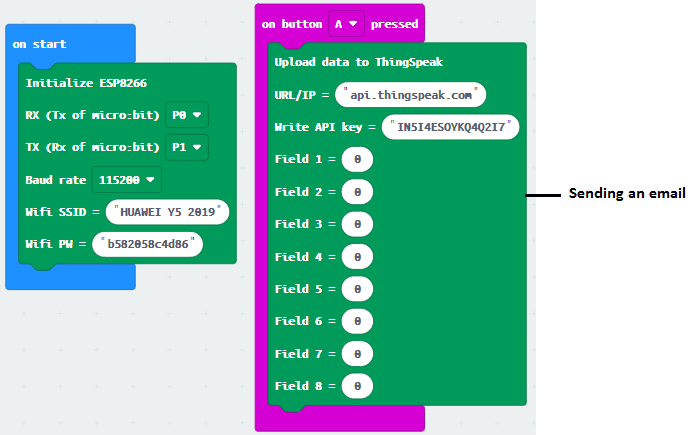
In this tutorial we will send an email when we press the A button on the Micro:bit card.
First, we must use the two ThingSpeak and IFTTT web services which allow sending an email by the Micro:bit card.
Then, we must have the ESP8266 wifi card which allows you to connect the Micro:bit card to the Internet by wifi.

Necessary components:
Micro:bit
The Micro:bit is a small, programmable microcontroller board designed to make learning to code and creating electronics projects accessible to beginners. It was developed by the BBC in partnership with a number of technology companies, with the goal of providing a simple, low-cost platform that could be used to teach kids how to code and create digital devices.
The Micro:bit is equipped with a number of sensors and input/output (I/O) devices, including an accelerometer, a compass, a thermometer, and two programmable buttons. It also features a 5×5 LED matrix that can be used to display text, images, and animations.
Users can program the Micro:bit using a variety of languages, including Python, JavaScript, and Microsoft Block Editor, and can also use it to control other devices and sensors via Bluetooth or USB. It can be powered by a USB cable or by a battery pack.
The Micro:bit board is widely used in schools and educational institutions, it is a good tool for learning the basics of coding and electronics.
Micro:bit GPIO card

The Micro:bit GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) card is an accessory for the Micro:bit microcontroller board that provides additional input and output pins for connecting to external devices and sensors. The card connects to the Micro:bit via the edge connector on the bottom of the board, and provides access to a variety of different types of I/O, including digital I/O, analog I/O, I2C, and SPI.
ESP8266 wifi

The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microcontroller module that is designed for IoT applications. It is based on the ESP8266 chip, which is a 32-bit microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi capabilities. The module is small, low-power, and easy to use, making it a popular choice for IoT projects.
The Micro:bit can be used in conjunction with the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module to create IoT projects that can connect to the internet and send or receive data. The Micro:bit acts as the main controller of the project, while the ESP8266 provides the Wi-Fi connectivity.
To use the ESP8266 with the Micro:bit, the ESP8266 module must be connected to the Micro:bit’s pins and then programmed using the Micro:bit’s software development environment. This can be done using the Micro:bit’s built-in support for the ESP8266, which allows the Micro:bit to communicate with the ESP8266 using a serial connection.
Once the connection is established, the Micro:bit can then send and receive data over Wi-Fi using the ESP8266. This allows the Micro:bit to connect to the internet and interact with other devices or services, such as sending sensor data to a cloud service or receiving commands from a smartphone app.
It is also possible to use the ESP8266 to create a standalone Wi-Fi access point and web server, this way the Micro:bit can be controlled remotely via a web interface.
5V/3.3V power supply module
A 5V/3.3V power supply module is a device that converts a higher voltage, typically 12V or 24V, into a lower voltage, usually 5V or 3.3V, which is required by most microcontrollers and other electronic devices. These modules are commonly used in projects that involve microcontrollers like the Arduino and Raspberry Pi, as well as in IoT and other electronic projects.
THE 5V/3.3V power supply module is particularly important when using the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module, as the ESP8266 requires a stable 5V power supply in order to function properly. The ESP8266 is a 5V device and using a power supply that is not providing the correct voltage can damage the device or cause it to malfunction.
Test plate

A test plate, also known as a prototyping plate or a breadboard, is a device that is used to build and test electronic circuits. It provides a convenient way to connect components such as resistors, transistors, and LEDs, without the need for soldering.
Connecting wires

Connecting wires are used to connect electronic components in a circuit. They are typically made of copper and are coated with insulating material to prevent electrical contact between the wires themselves or between the wires and other conductive materials.
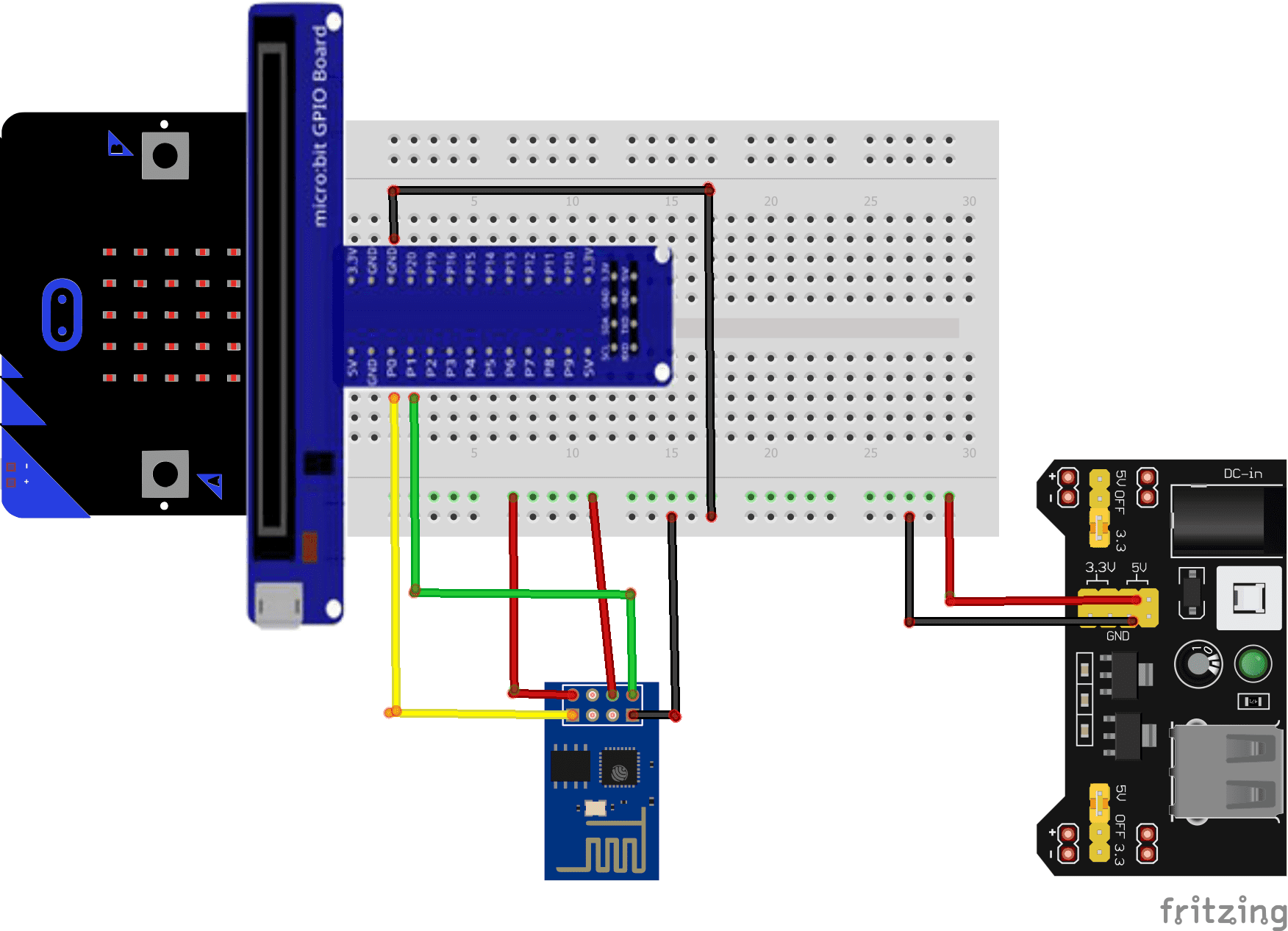
Mounting:
To perform the assembly, you can connect
-
The RX pin of the ESP8266 card to Pin P0 of the Micro:bit card
-
The TX pin of the ESP8266 card to Pin P1 of the Micro:bit card
-
The GND pin of the ESP8266 board to the GND of the Micro:bit board
-
The two pins 3V3 and EN of the ESP8266 board to the 5V pin of the power supply module
Makecode Program:















jason 16-12-2121
HI This is only the first step in the process I assume you are using IFTTT to monitor the ThingSpeak account & send a preset email to a preset email address when it detects some data being sent? Maybe it would be helpful to show the rest of the process as someone new to IOT may not realise what is involved?